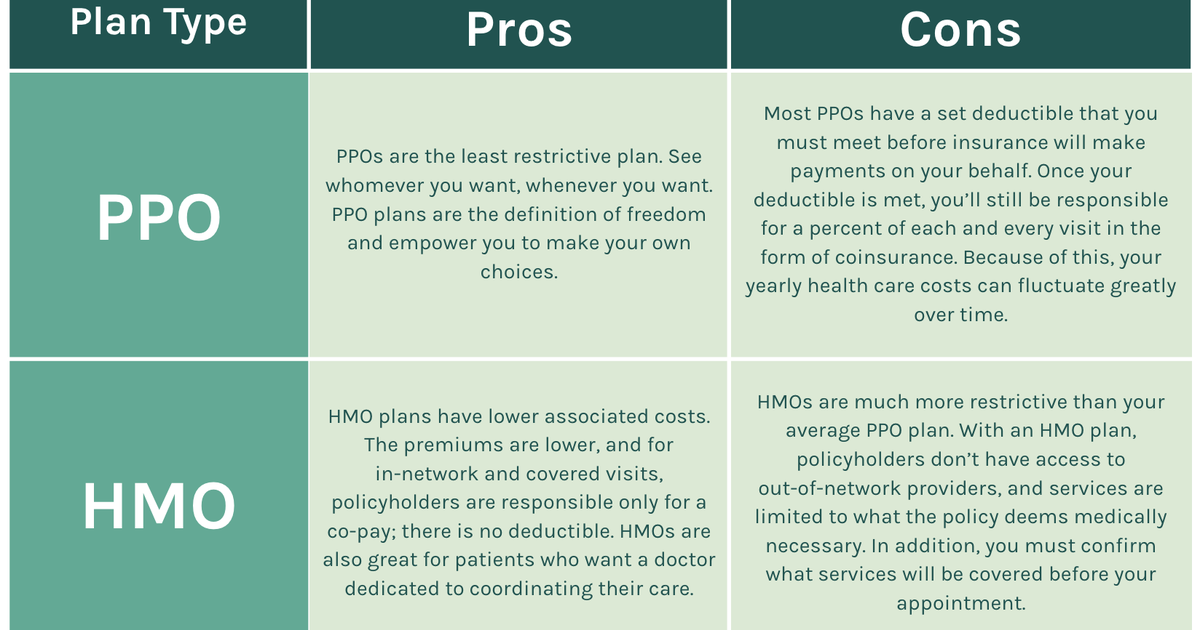
Navigating the healthcare insurance landscape can be a daunting task, particularly when faced with the choice between HMO and PPO plans. Both offer coverage, but their structures and intricacies can significantly impact your healthcare experience. This guide delves into the fundamental differences between these two common plan types, shedding light on key aspects such as network access, cost, and administrative processes.
Understanding the nuances of HMO and PPO plans is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. This article serves as a comprehensive resource, empowering you with the knowledge needed to select the plan that best aligns with your individual needs and preferences.
Navigating the Healthcare Insurance Landscape: HMO vs. PPO
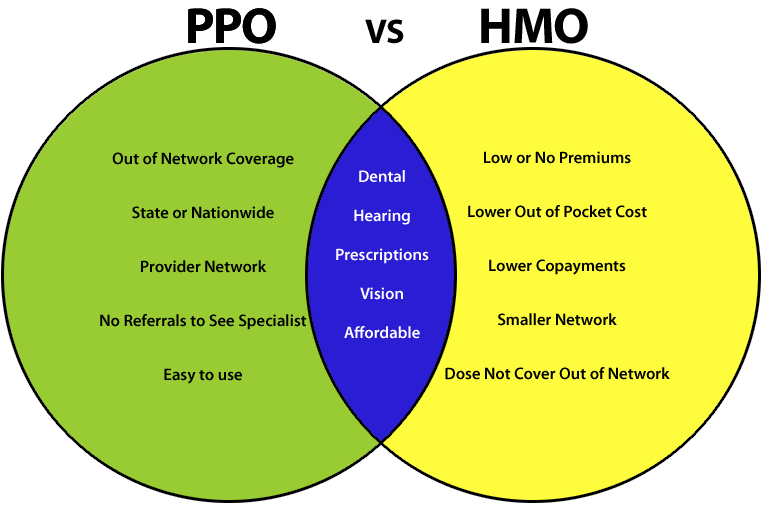
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be a daunting task, especially with the numerous options available. Two of the most common types of plans are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). Understanding the key differences between these plans is crucial for making an informed decision that best suits your individual needs and budget.
Defining HMO and PPO
Both HMO and PPO plans provide coverage for medical expenses, but they differ in their network structure, cost-sharing mechanisms, and flexibility.
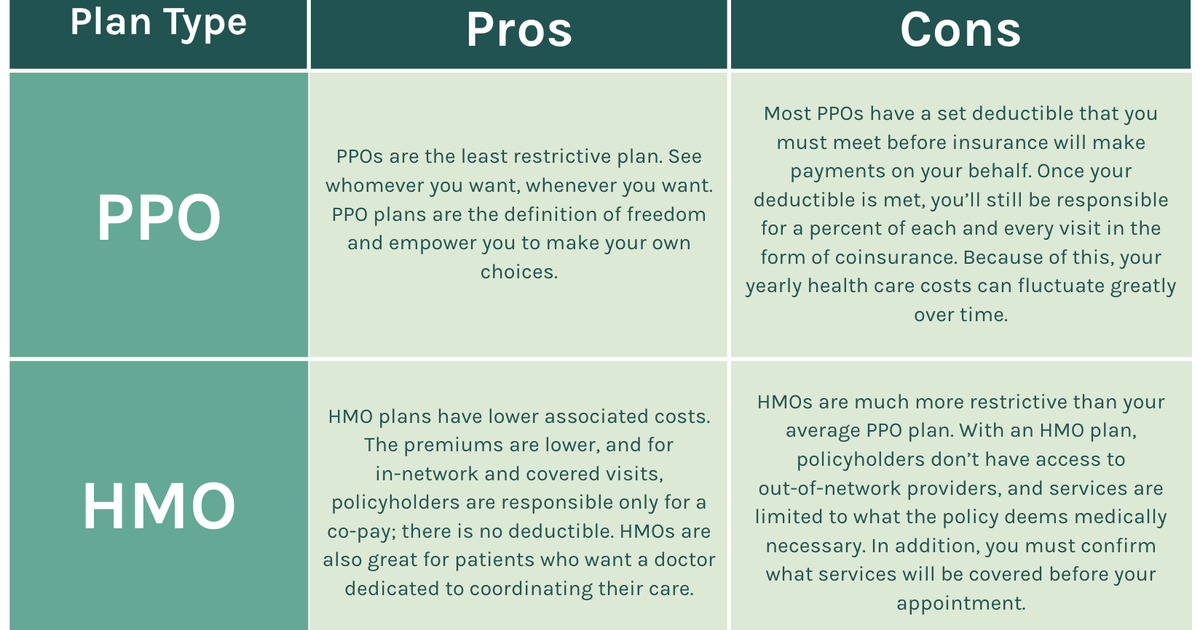
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): An HMO operates on a managed care model, emphasizing preventive care and cost-efficiency. Members typically choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the HMO’s network, who acts as a gatekeeper to specialist referrals.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): A PPO offers more flexibility than an HMO, allowing members to see providers both within and outside the network. However, out-of-network services generally come with higher costs.
Understanding the Healthcare Insurance Landscape
The healthcare insurance landscape has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by factors such as technological advancements, rising healthcare costs, and evolving consumer preferences. This evolution has led to the emergence of various plan types and coverage options, each catering to different needs and financial situations.
Network Structure and Access
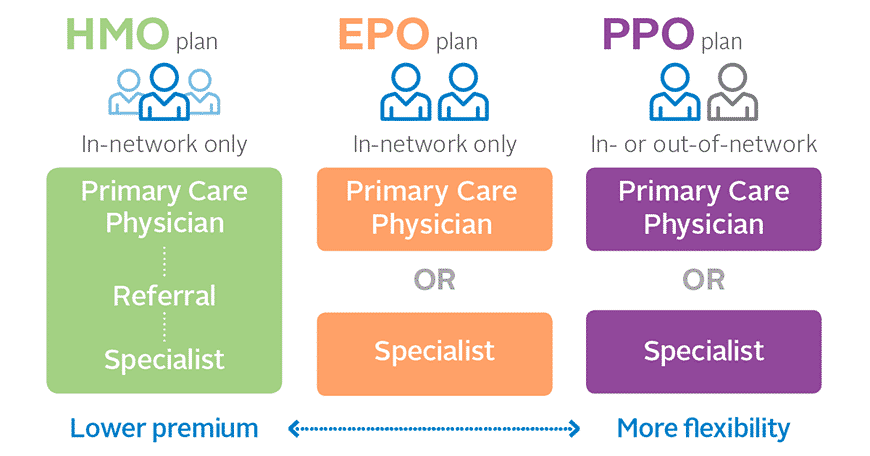
The network structure of a health insurance plan determines the healthcare providers you can access. Understanding the difference between HMO and PPO networks is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions.
Network Structure
HMO and PPO plans differ significantly in their network structures. HMOs operate with a closed network, meaning they have a specific list of providers who are contracted with the plan. PPOs, on the other hand, utilize an open network, allowing members to choose from a broader range of providers, including those both in and out of the network.
In-Network and Out-of-Network Providers
- In-network providers are healthcare professionals who have contracts with the insurance plan. They agree to provide services at pre-negotiated rates, which are generally lower than out-of-network rates.
- Out-of-network providers are those who do not have contracts with the insurance plan. They are not bound by the plan’s pre-negotiated rates and may charge significantly higher fees.
Implications of Network Choice
- HMOs: Choosing an in-network provider is essential for maximizing coverage and minimizing out-of-pocket costs. If you seek care from an out-of-network provider, you will likely face significant financial burdens, including higher copays and deductibles.
- PPOs: PPOs offer more flexibility. While using in-network providers is generally recommended for cost-effectiveness, PPOs allow you to see out-of-network providers with higher out-of-pocket costs. However, you may need to file a claim for reimbursement, which can be time-consuming.
Cost and Coverage
The cost of healthcare insurance plans can vary significantly, depending on factors such as the type of plan, coverage level, and individual circumstances. Understanding the cost structure of HMO and PPO plans can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
Premium Costs
Premiums are the monthly payments you make to maintain your health insurance. HMO plans generally have lower premiums than PPO plans. This is because HMOs typically have a narrower network of providers, which allows them to negotiate lower rates with healthcare professionals. PPO plans, with their wider networks, often have higher premiums to accommodate the broader range of providers.
Deductibles
Deductibles are the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. HMO plans typically have lower deductibles than PPO plans. This means you will start paying for covered services sooner with an HMO plan, but you will pay more in premiums. PPO plans, with their higher deductibles, often have lower premiums, allowing you to pay less upfront but potentially more overall.
Copayments
Copayments are fixed amounts you pay for each medical service you receive. Both HMO and PPO plans have copayments, but the specific amounts can vary depending on the service. HMO plans often have lower copayments than PPO plans for in-network services, but they may have higher copayments for out-of-network services. PPO plans, on the other hand, may have higher copayments for in-network services but lower copayments for out-of-network services.
Coverage Levels
HMO and PPO plans offer different levels of coverage for various medical services.
Preventive Care
Both HMO and PPO plans typically cover preventive care services, such as annual checkups, screenings, and vaccinations, at no cost to the insured.
Hospitalization
HMO plans generally cover hospitalization services within their network, but they may require pre-authorization for certain procedures. PPO plans, with their broader networks, offer more flexibility in choosing hospitals, but they may have higher copayments or deductibles for out-of-network services.
Prescription Drugs
Both HMO and PPO plans typically cover prescription drugs, but the coverage levels and formularies (lists of covered drugs) can differ. HMO plans often have a narrower formulary than PPO plans, meaning they may cover fewer drugs. However, HMO plans may offer lower copayments for drugs on their formulary. PPO plans, with their broader formularies, may have higher copayments for drugs on their formulary.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses are the costs you incur for healthcare services that are not covered by your insurance. These expenses can include deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and charges for services not covered by your plan. HMO plans typically have lower out-of-pocket expenses for in-network services, but they can have higher out-of-pocket expenses for out-of-network services. PPO plans, with their broader networks, may have higher out-of-pocket expenses for in-network services, but they can have lower out-of-pocket expenses for out-of-network services.
It is important to note that out-of-pocket expenses can vary significantly depending on the specific plan and the services you receive.
Choice and Flexibility
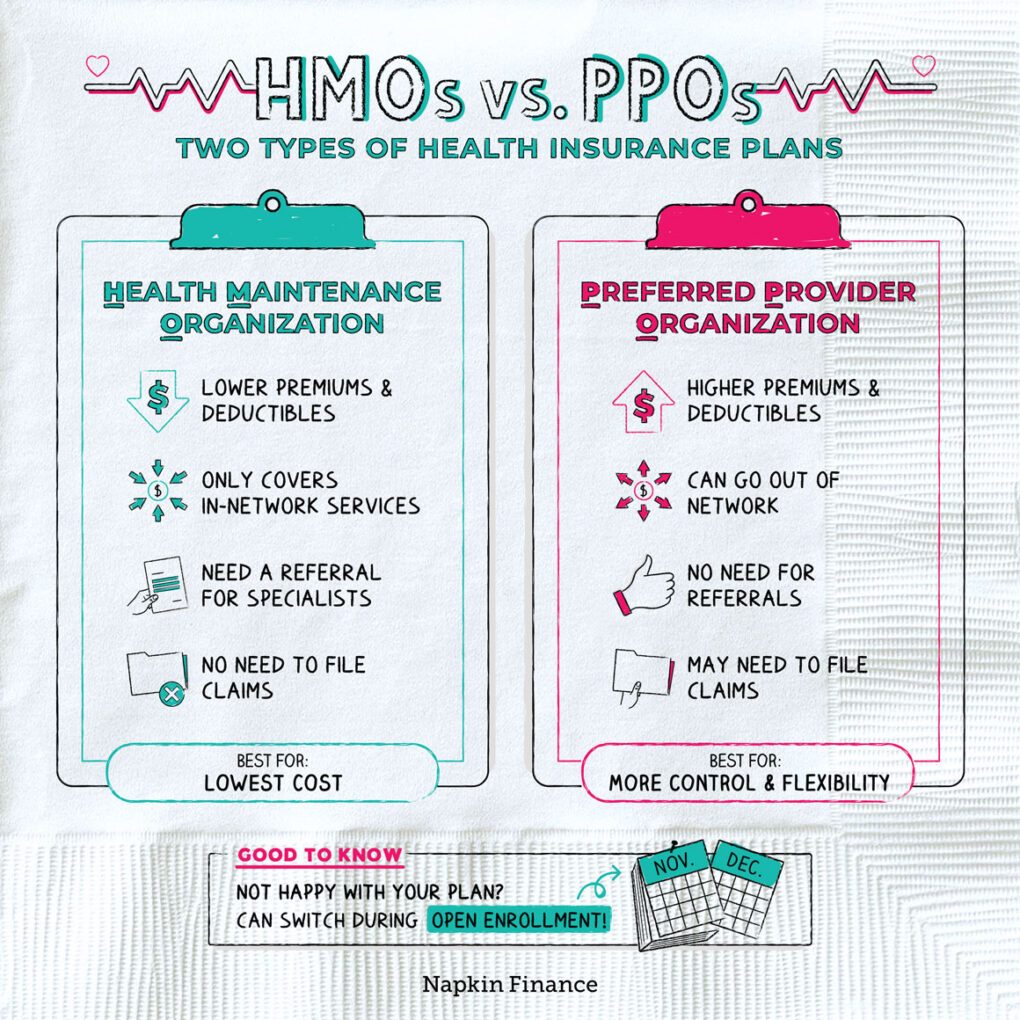
The choice and flexibility offered by different healthcare plans are key considerations for individuals seeking coverage. While both HMO and PPO plans provide access to healthcare services, their structures differ significantly, impacting the patient’s ability to choose providers and navigate the healthcare system.
Provider Choice and Network Structure
HMOs, or Health Maintenance Organizations, operate within a closed network of providers. This means that members must receive care from doctors and specialists within the HMO’s network. This can limit choice, but it often results in lower premiums. PPOs, or Preferred Provider Organizations, offer more flexibility. While PPOs also have a network of providers, members can see out-of-network doctors, though they will typically pay higher out-of-pocket costs.
Referral Process and Primary Care Physicians
HMOs generally require a referral from a primary care physician (PCP) to see specialists. This means that patients must first consult with their PCP, who will then refer them to a specialist if necessary. PPOs typically do not require referrals, allowing patients to see specialists directly. However, PPOs may have higher copayments for out-of-network specialists.
Patient Autonomy and Healthcare Decision-Making
The referral process and network structure have significant implications for patient autonomy and healthcare decision-making. HMOs can limit patient choice by restricting access to out-of-network providers, while PPOs offer more flexibility but may result in higher out-of-pocket costs. This can impact patients’ ability to access the care they need and their ability to make informed healthcare decisions.
Administrative Processes
Navigating the administrative aspects of healthcare insurance can be a significant factor in overall patient satisfaction and healthcare efficiency. Understanding the administrative processes associated with HMO and PPO plans can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
Gatekeepers and Pre-Authorization
The administrative processes associated with HMO and PPO plans differ significantly, particularly in terms of gatekeepers and pre-authorization procedures.
HMOs typically employ a gatekeeper system, usually a primary care physician (PCP), who acts as the first point of contact for members seeking healthcare services. A PCP serves as a coordinator, referring patients to specialists or other healthcare providers within the network as needed. This approach aims to manage costs and ensure appropriate care.
PPOs, on the other hand, generally do not require a PCP referral for specialist visits. Members can choose their healthcare providers, including specialists, directly within the network. However, pre-authorization procedures may be necessary for certain services, such as elective surgeries or expensive treatments, to ensure that the service is medically necessary and covered under the plan.
Claim Processing
The claim processing procedures also differ between HMO and PPO plans. HMOs often have a more streamlined claim processing system due to their managed care approach. Claims are typically submitted electronically, and the HMO processes them directly, often with a faster turnaround time.
PPOs, with their greater flexibility in provider choice, have a more decentralized claim processing system. Members may submit claims directly to the provider, who then submits them to the PPO for processing. This process can be more complex and may take longer to complete.
Impact on Patient Experience and Healthcare Efficiency
The administrative processes associated with HMO and PPO plans can significantly impact patient experience and healthcare efficiency.
HMOs, with their emphasis on cost control and coordinated care, can often lead to shorter wait times for appointments and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
However, the gatekeeper system can sometimes create barriers to accessing specialists or specific treatments, potentially leading to delays in care.
PPOs, with their greater provider choice and flexibility, can provide patients with greater control over their healthcare decisions.
However, the more complex claim processing procedures and the potential need for pre-authorization can create administrative burdens for patients and providers, potentially leading to increased costs and delays in care.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO plan involves weighing the pros and cons of each. Understanding the specific advantages and disadvantages of each plan type can help you make an informed decision based on your individual healthcare needs and preferences.
HMO Advantages and Disadvantages
HMO plans often come with lower monthly premiums compared to PPO plans. This can be a significant advantage for individuals and families seeking to minimize their healthcare costs. However, HMO plans typically have more restrictive network structures and require referrals from primary care physicians for specialist visits.
Advantages
- Lower Premiums: HMO plans generally have lower monthly premiums compared to PPO plans, making them a more budget-friendly option. For example, a family of four might save hundreds of dollars per year by choosing an HMO plan over a PPO plan with similar coverage.
- Preventive Care Emphasis: HMOs often emphasize preventive care services, offering screenings and check-ups at no additional cost. This can lead to early detection of health issues and potentially reduce the need for more expensive treatments in the future.
- Integrated Care: HMOs often have a coordinated approach to care, with a focus on primary care physicians as the gatekeepers to specialists. This can streamline care and ensure that patients receive comprehensive treatment.
Disadvantages
- Limited Network: HMO plans typically have a narrower network of healthcare providers compared to PPO plans. This means you may have fewer choices when selecting a doctor or hospital, and you might need to travel further to access care.
- Referral Requirements: HMO plans generally require referrals from your primary care physician to see specialists. This can add an extra step to the process and potentially delay treatment, especially if your primary care physician is unavailable or has a long wait time.
- Limited Out-of-Network Coverage: HMO plans typically do not cover out-of-network services except in emergencies. This means you will likely have to pay significantly higher out-of-pocket costs if you need care from a provider outside of your network.
PPO Advantages and Disadvantages
PPO plans provide greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, offering access to both in-network and out-of-network providers. However, they generally have higher monthly premiums and copayments compared to HMO plans.
Advantages
- Wider Network: PPO plans have broader networks of healthcare providers, giving you more choices when selecting a doctor or hospital. This can be especially beneficial if you prefer a specific specialist or have a strong preference for a particular hospital.
- No Referral Requirements: PPO plans typically do not require referrals from a primary care physician to see specialists. This allows you to access specialized care more quickly and efficiently.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: PPO plans typically offer some coverage for out-of-network services, though at a higher cost. This provides you with more flexibility in accessing care, especially if you need to see a specialist who is not in your network.
Disadvantages
- Higher Premiums: PPO plans generally have higher monthly premiums compared to HMO plans. This is due to the broader network and out-of-network coverage offered by PPO plans.
- Higher Copayments: PPO plans often have higher copayments for services compared to HMO plans. This means you will have to pay more out-of-pocket for each visit or procedure.
- Less Emphasis on Preventive Care: PPO plans may not have the same emphasis on preventive care services as HMO plans. This could lead to higher healthcare costs in the long run if health issues are not detected and treated early.
HMO vs. PPO: A Comparison
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Premiums | Lower | Higher |
| Network Size | Narrower | Wider |
| Referral Requirements | Required | Not Required |
| Out-of-Network Coverage | Limited | Available, but at higher cost |
| Preventive Care Emphasis | High | Moderate |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan can be a complex process, especially when considering the differences between HMO and PPO options. To make an informed decision, individuals should carefully weigh various factors that align with their unique healthcare needs and preferences.
Factors to Consider
Understanding your healthcare needs and preferences is crucial for choosing the best plan.
- Health Status and Healthcare Needs: Evaluate your current health conditions, potential future needs, and frequency of healthcare visits. Individuals with chronic conditions or who require frequent medical attention may benefit from a PPO plan, which offers greater flexibility in choosing providers. Conversely, those with generally good health and limited healthcare needs might find an HMO plan sufficient.
- Geographic Location and Provider Network: Consider the geographic location of your preferred healthcare providers and ensure they are included in the plan’s network. HMO plans typically have smaller networks, while PPO plans offer wider provider choices.
- Cost and Coverage: Carefully analyze the premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance associated with each plan. HMO plans generally have lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, while PPO plans offer greater flexibility but may come with higher premiums.
- Flexibility and Choice: Evaluate the level of flexibility and choice you desire in selecting healthcare providers and accessing services. HMO plans require referrals for specialist visits, while PPO plans allow you to choose specialists directly.
- Administrative Processes: Consider the administrative processes involved in each plan, such as pre-authorization requirements, claim processing procedures, and customer service responsiveness.
Questions to Ask Yourself and Your Healthcare Provider
Asking yourself these questions and seeking guidance from your healthcare provider can further inform your decision.
- What are my current and potential future healthcare needs?
- How often do I typically visit healthcare providers?
- Do I have any specific healthcare providers I prefer?
- What is my budget for healthcare expenses?
- What are the pros and cons of each plan in relation to my specific needs?
Practical Tips for Navigating the Healthcare Insurance Landscape
Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be overwhelming.
- Start early: Begin researching plans well before your open enrollment period to allow sufficient time for comparison and decision-making.
- Utilize online resources: Leverage online comparison tools and resources provided by insurance companies and independent organizations to gather information and compare plans.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with a qualified insurance broker or healthcare advisor to gain personalized guidance and support in selecting the right plan.
- Read the fine print: Carefully review the plan’s details, including coverage limitations, exclusions, and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of changes in healthcare laws and regulations that may impact your coverage.
Real-World Examples
To gain a deeper understanding of the practical implications of HMO and PPO plans, let’s examine real-world experiences of individuals who have navigated both types of health insurance. By analyzing their experiences, we can highlight the key differences they encountered in terms of cost, coverage, and access to care, and explore the potential impact of these experiences on their healthcare choices and outcomes.
Comparative Experiences
Understanding the real-world implications of HMO and PPO plans requires examining individual experiences. Here are two examples:
- Sarah, a young professional with a chronic condition: Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer, was diagnosed with Crohn’s disease at 25. Initially, she had an HMO plan that required her to see a primary care physician (PCP) for referrals to specialists. However, her PCP was unfamiliar with Crohn’s disease and often referred her to specialists outside her network. This led to higher out-of-pocket costs and difficulty accessing timely care. When Sarah switched to a PPO plan, she found greater flexibility in choosing specialists, allowing her to see a gastroenterologist who specialized in Crohn’s disease. This resulted in improved access to care and a more personalized treatment plan, ultimately leading to better management of her condition.
- John, a retiree with multiple health concerns: John, a 65-year-old retired teacher, had an HMO plan for several years. He found it difficult to access specialists, often having to wait for weeks for appointments. His plan also had limited coverage for certain medications, leading to high out-of-pocket costs. After retiring, John switched to a PPO plan, which offered him greater flexibility in choosing providers and a wider network of specialists. He was able to see a cardiologist and an orthopedic surgeon without needing a referral from his PCP. While his PPO plan had higher monthly premiums, John found the increased access to care and broader coverage worth the extra cost.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of healthcare insurance can be a daunting task, especially when faced with the choice between HMO and PPO plans. While both offer coverage, their distinct structures and features cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with individual circumstances.
Key Takeaways
The choice between an HMO and a PPO boils down to a balance between cost, access, and flexibility. HMOs typically offer lower premiums but restrict access to a specific network of providers. PPOs, on the other hand, provide greater flexibility with wider networks and out-of-network coverage, but at a higher cost.
Ultimately, the best plan depends on individual factors such as health status, location, budget, and desired level of choice.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Given the intricate nature of healthcare insurance, consulting with a qualified healthcare insurance expert is highly recommended. These professionals can provide personalized guidance based on individual circumstances, ensuring the chosen plan effectively meets specific needs and budget constraints.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, the choice between an HMO and a PPO boils down to individual priorities and circumstances. Factors like cost, provider choice, and administrative ease should be carefully weighed. Consulting with healthcare insurance experts can provide valuable guidance in navigating the complexities of these plans and ensuring you secure the most suitable coverage for your healthcare journey.